Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) is the process of managing the complete lifecycle of a product from the beginning, through engineering design and manufacture, to service and removal of manufactured products.
Product Lifecycle Management:
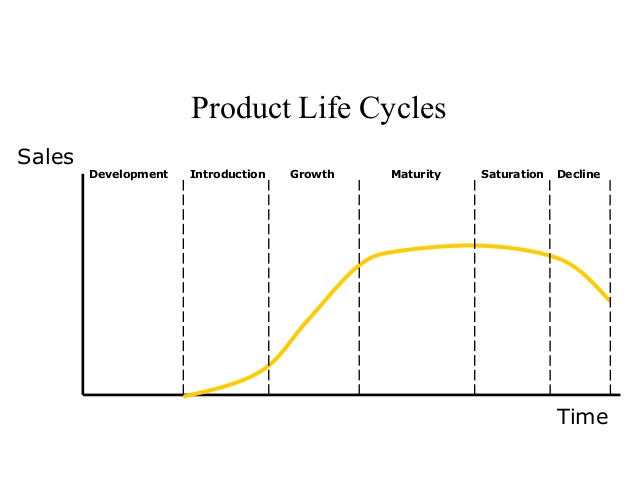
Product Lifecycle Management is linked with marketing and management decisions within businesses, and all products go through five primary stages:
Development, Introduction, Growth, Maturity, and Decline
Each stage has its costs, opportunity, and risks, and entity products differ in how long they remain at any of the life cycle stages.
1. Development
The product development stage is often referred to as “the valley of death.” At this stage, costs are accumulating with no parallel income.
Some products require years and large capital investments to develop and then test their efficiency. This stage is typically funded by the entrepreneur from their own personal resources.
2. Introduction
The introduction stage is about developing a market for the product and building product consciousness. Marketing costs are high at this stage. This is also the stage where intellectual property rights protection is obtained.
3. Growth
In the growth stage, the product has been accepted by customers, and companies are striving to increase market share. For innovative products, there is limited competition at this stage, so pricing can remain at a higher level.
Both product demand and profits are increasing, and marketing is aimed at a broad audience. Funding for this stage is generally still through lenders or through increasing sales revenue.
4. Maturity
At the mature stage, sales will level off. Competition increases, so product features may need to be enhanced to maintain market share.
While unit sales are at their highest at this stage, prices tend to decline to stay competitive. Companies usually do not need additional funding at this stage.
5. Decline
The decline stage of the product life cycle is associated with decreasing revenue due to market saturation, high competition, and changing customer needs.
Companies at this stage have several options: They can choose to discontinue the product, sell the manufacturing rights to another business that can better compete or maintain the product by adding new features, finding new uses for the product, or tapping into new markets through exporting.
This is the stage where the packaging will often announce “new and improved.”
Essential Elements of Product Lifecycle Management (PLM):
- Manages design and process documents
- Offers an electronic file repository
- Includes built-in and custom parts and document metadata (“attributes”)
- Identifies materials content for environmental compliance
- Constructs and controls bill of material (product structure) records
- Permits item-focused task assignments
- Enables workflow and process management for approving changes
- Controls multi-user secured access, including “electronic signature”
- Exports data for downstream ERP systems